Other Cell Applications
The application specific pages describe cell isolation protocols for common applications. VitaCyte shares these methods because the critical steps are described in detail and have been used successfully by multiple laboratories. VitaCyte does not have recommended protocols for many other cell types. However, we can recommend a process for using available information in the literature along with current VitaCyte products to help identify a formulation that will work for the target cell type.
Replicating most cell isolation protocols for other cells can be challenging for several reasons.
Critical steps in the cell isolation method are performed differently.
The tacit or unwritten knowledge of the cell isolator cannot be explicitly written or shared with others in a documented manner.
Lot to lot differences in the collagenase products used by different laboratories.
Modifications are made to reported methods, but those improvements are not recorded or published.
If your goal is to adopt a new cell isolation procedure or find an alternative to your current method, the best place to begin is to search journals or online websites that publish life science protocols. You can also contact your university library to get access to other journals that focus on publishing life science protocols.
Collagenase-Protease Mixtures for Cell Isolation
Selection of the collagenase-protease mixture is crucial in enzyme-mediated cell isolation as it affects cell viability, yields, and function of the cells isolated from tissue. The most common approach is to pre-qualify available, “off the shelf” traditional crude of enriched collagenase products by evaluating several lots. The goal is to select the lot of collagenase (i.e., the “good lot”) that effectively isolates the cells of interest. Once identified, the end-user buys enough of the good lot to last a year or more.
VitaCyte’s purified-defined enzymes offer significant advantages over the traditional crude and enriched enzymes as summarized in the table below.
| Traditional Collagenase | VitaCyte Purified-Defined Collagenase | |
|---|---|---|
| Lot Consistency | Minimal: Each lot unique | Maximal: Use of purified enzymes ensures consistency |
| Collagenase Purity | 4-8% (w/w) for crude 15-25% (w/w) for enriched | > 95% (w/w) |
| Need to Pre-Qualify New Collagenase Lots | Necessary to optimize isolation procedure | No need after initial optimization step performed |
| Replication of Results in Other Labs | ? less likely if good lots hard to find | No problem, enzyme composition defined |
| Additional Modification of Enzyme Formulation | Not possible | Always an option |
The difference in lot consistency reflects the lower purity of traditional collagenase products and the potential for other biochemical components in the product to influence cell viability or function. This explains why most end-users pre-qualify new lots of traditional collagenase. If purified collagenase and protease enzymes are used in their place, then lot pre-qualification procedures is eliminated, after defining the activities in an optimal enzyme mixture for a specific application, then the same product can be ordered again. Moreover, further adjustments in the enzyme composition can readily be made after the enzyme activities are defined.
Product UseVitaCyte’s Rational Design Method for Tissue Dissociation Enzyme (RDMTDE) Optimization
VitaCyte’s RDMTDE optimization method for formulating enzyme mixtures applies principles from a hypothetical model for enzyme mediated cell isolation described elsewhere. This model simplifies optimization of collagenase-protease enzyme mixtures because it assumes that if collagenase’s collagen degradation activity (CDA) is in excess, then the focus of the optimization procedure should be on neutral protease activity. Under conditions of excess CDA, neutral protease activity impacts digestion time, cell yield, viability and detection of cell membrane markers used to characterize the cell population.
PD Collagenase 800
Cat # 011-3020
Collagenase Gold
Cat # 011-1060
Four Key Assumptions of the Enzyme-Mediated Cell Isolation Model
ASSUMPTION ONE
Excess purified collagenase (with minimal protease contamination) will not have an adverse effect on cell viability or function
ASSUMPTION TWO
Collagenase’s collagen degradation activity (CDA) must be in excess to ensure loosening of the extracellular matrix
ASSUMPTION THREE
If CDA in excess, then neutral protease activity controls the speed of tissue digestion, and yield of functional, viable cells
ASSUMPTION FOUR
Neutral protease activity required for successful cell isolation is equivalent or less than the neutral protease activity found in Worthington Type 1 collagenase
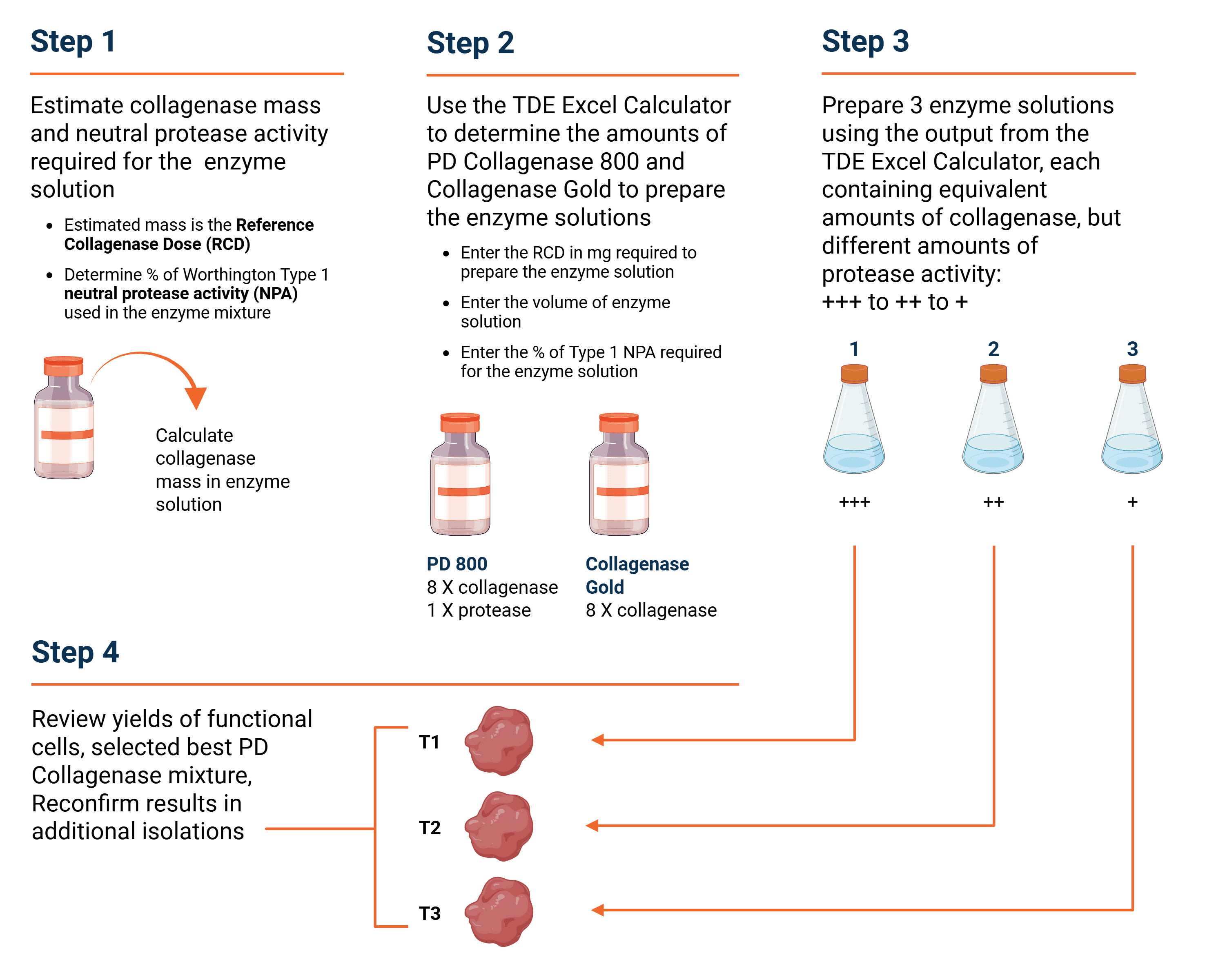
Method Overview
Created in https://BioRender.com
Note, PD Collagenase 800 and Collagenase Gold contain the same amount of collagenase. Only PD Collagenase 800 contains neutral protease activity. This activity is close to the activity found in a 1 g bottle of Worthington Collagenase Type 1. The broad application of Type 1 Collagenase to digest any mammalian tissue means that referencing the enzyme mixture to the percentage of neutral protease activity found in Type 1 Collagenase provides a helpful reference point.
For specific details consult the package inserts.
Estimate the mg of collagenase and the neutral protease activity required for the enzyme solution. This amount is referred to as the Reference Collagenase Dose (RCD) .If you do not know the neutral protease activity, assume that 100% of the Worthington Collagenase Type 1 activity is sufficient for cell isolation. It is useful to prepare several enzyme solutions with decreasing neutral protease activities to assess its effect on functional cell yield and viability.
Use the TDE Excel Calculator to determine the amounts of PD Collagenase 800 and Collagenase Gold to prepare the enzyme solutions. Enter the mg of collagenase, mL of enzyme solution, and percentage of Worthington Collagenase Type 1 neutral protease activity required to prepare each enzyme solution.
Determine if VitaCyte’s products provide comparable results to those obtained using the current collagenase enzyme. You may find slower digestion times as the neutral protease activity is decreased as would be expected from the hypothetical model of enzyme-mediated cell isolation. You will need to determine if extending the digestion time provides other benefits to the recovered cell population.
Reviewing Results
If the results are comparable to those obtained with your current lot of product, congratulations! You now know more about the enzyme formulation required for isolating your cell of interest.
If you do not obtain equivalent results with any of the enzyme mixtures above when compared to your current lot of collagenase, the enzyme formulation may need to adjusted or supplemented with another protease. Clostripain may be needed because it has a complementary enzyme activity compared to BP Protease. Clostripain is a trypsin-like enzyme that cuts at different regions of the protein than BP Protease.
The effort required to assess the performance of the three enzyme solutions above will not change your effort to qualify new lots of traditional crude or enriched collagenase products. The benefits of adopting the PD Collagenase enzymes in place of traditional collagenase are summarized in the table below.
| Lot Qualification | PD Optimization | |
|---|---|---|
| Effort Required | Equivalent | Equivalent |
| Knowledge Gained | None, no knowledge of enzyme composition | Essential: Enzyme composition defined |
| Lot Pre-Qualification | No change, must prequalify new lots | Once defined, no need to prequalify future lots |
| Ability to Modify Formulation | None | Yes |
| Shelf Stability for Product | ? | 4 years |
If you have any questions on using enzymes for cell isolation or recovery, contact VitaCyte Technical Support.
TDE Excel Calculator
Fill out the form below to verify your email and then the excel calculator will be sent to you.